Red Flags
Diagnosis is key
To reduce morbidity, choose the best treatment option and limit recurrence and / or complications.
Most of the symptoms seen in patients with acute uncomplicated cystitis are typical but not specific

The Acute Cystitis Symptom Score (ACSS) questionnaire is used to:
- Promote (self-) diagnosis and seek for medical advice
- Help differentiate from other urogenital disorders
- Assess the severity and impact on QOL
- Monitor treatment efficacy
Some patient profiles are more at risk / prone to recurrence.
Use the LUTIRE test to
predict your patient’s risk
Women who:

- Sexually active women (risk increases with number of partners)
- Gram-negative pathogen infections
- Postmenopausal women
- Constipation
- Previous treatment of ABU
Side effects

- Most common: antibiotic-associated diarrhoea (2–25%)
- Antibiotic prophylaxis studies are generally old and efficacy results might be outdated due to increasing rates of resistance, as well as unlisted side effects due to their broader, prolonged or chronic use, including collateral damages
Aminopenicillins & fluroquinolones
(Should not be used)
- No longer suitable for antimicrobial therapy of uncomplicated UTIs because of negative ecological effects and high resistance rates worldwide
- Fluoroquinolones can also have serious side effects including tendon rupture, psychological and cardiac issues
Fosfomycin
- Serious adverse events such as aplastic anaemia, anaphylaxis, and liver toxicities are infrequently reported
- The most frequently reported adverse events are rash, peripheral phlebitis, hypokalaemia and gastrointestinal disorders
Nitrofurantoin
- Increased risk for adverse events (neurogenic, hepatic and pulmonary) compared to trimethoprim and methenamine
- Should be used with caution in those with renal impairment
- Should be avoided at term in pregnancy (risk of neonatal haemolysis)
- Adults (especially the elderly) and children on long-term therapy should be monitored for conditionally used liver function and pulmonary symptoms
Trimethoprim (conditionally)
- Causes teratogenic risk in the 1st trimester of pregnancy and is contraindicated in pregnant women
- Trimethoprim is usually prescribed as Co-trimoxazole, which has the following adverse effects: dermatological, hematological and gastrointestinal side effects, without providing an acceptable added benefit
Sulfamethoxazol
- which has the following side effects: dermatological, hematological and gastrointestinal side effects, without providing additional benefit
Antimicrobial resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health
- Accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics, as well as poor infection prevention and control
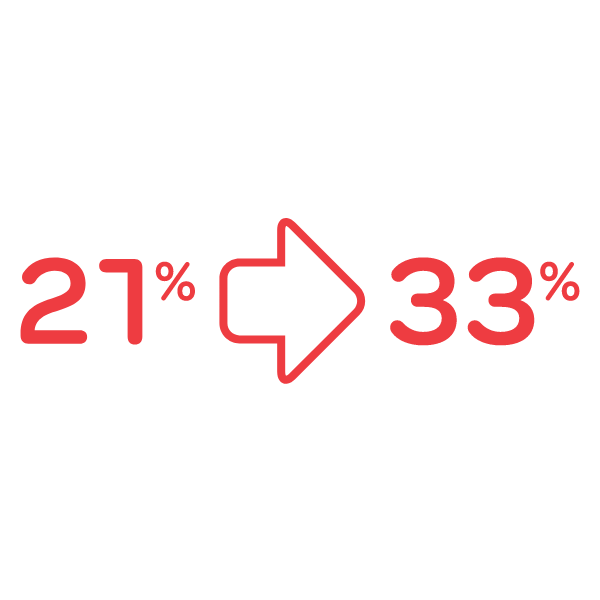
- 25% of all antibiotic prescriptions are for UTIs
- Costs the European Union €1.5 billion in healthcare expenses and lost productivity each year
- Can lead to more severe infections, longer hospital stays and increased mortality
- Some infections for which therapy is now available might become untreatable
Alternatives to antimicrobials for the prevention of rUTIs aim to reduce the crisis of antimicrobial resistance and pave the way for a new era in the management of rUTIs.
Bacterial reservoirs
- Infecting strains can invade bladder epithelial cells (forming bacterial reservoirs) and subsequently re-emerge to infect the bladder and cause another case of cystitis
- The main disease reservoirs for urogenital infections are the vagina and the gut, but reservoirs can also be found in the urethra
- In UTIs caused by uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC), more than 60% of recurrences can be attributed to the original infecting strain
What links antimicrobials to bacterial reservoirs and rUTIs?
- A decrease in peroxide-producing Lactobacillli may predispose pathogenic enteric bacteria to increased colonisation
- Formation of intracellular bacterial communities not sensitive to antibiotics
- A change in the glycosaminoglycan barrier of the urothelium, which may make an individual more susceptible to enteropathogenic infection
Microbiome impairment
- A resident microbial community in the human urinary tract has recently been identified, consisting of many genra and species, such as Lactobacillus crispatus
- Commensal species within the urinary and urogenital tract that are part of the local microbiota may act to protect against colonisation with uropathogens for bacterial displacement
- Both the infection itself and treatment strategies, such as antimicrobial therapy, can disrupt the urinary microbiome and affect the local immune homeostasis and healthy status
Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic options for the management of UTIs may soon incorporate efforts to measure, restore and/or preserve the native, healthy ecology of the urinary microbiota.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
What are the risk factors for development of AKI in UTI patients?
- Diabetes mellitus
- Upper UTI
- Febrile or septic shock during hospitalisation
- Impaired baseline renal function
Physicians should pay extra attention to UTI patients at risk of AKI.
What are the risk factors for pyelonephritis?
- Anatomic abnormalities fo urinary tract urolithiasis
- Diabetes mellitus
Patients with recurrent upper UTIs should be referred for further specialist investigation and management.
What factors can cause septic shock among UTI patients?
- Health care-associated infection
- Indwelling urinary catheter use
- Congestive heart failure
- Liver cirrhosis
- History of coronary artery disease
- AKI
Recognition of risk factors for complications and treatment failure with early intervention of broad-spectrum antimicrobials may significantly improve the outcome of sepsis in UTI patients.
Quality of life
- Although uncomplicated cystitis in women is considered to be a relatively benign and self-limiting condition, it can have a substantial negative effect on patients.
- Any illness, even if short-lived and not life threatening, can have an important impact on the patient’s daily activities, social functioning and wellbeing.
- The sudden, unforeseeable, and distressing nature of painful UTI episodes often cause patients anxiety. The resulting social handicap can lead to clinical symptoms of depression.
- Acute cystitis, as well as failure of the treatment, and adverse effects of antibiotics can reduce women’s quality of life.
As UTIs seem to be independently associated with a negative impact on quality of life or poor subjective wellbeing, more focus is needed on prevention, diagnosis and treatment of UTIs.